We have a wdio-based automation project that does end-to-end functional testing. We use CircleCI as the CI/CD tool to run automation regression. When setting up a project with CircleCI, we need to enter all configuration details in the config.yml file under the .circleci folder. Earlier, we only had staging regression and prod regression jobs and their respective workflows in the config.yml file.
As mentioned in this article, we also started doing screenshot testing for our application. With time, our configuration file expanded and became cluttered, accommodating various workflows like staging sanity, staging regression, prod regression, performance score testing, and screenshot testing jobs.
We explored various approaches to reduce the size of our configuration file. Later, we came across the Dynamic Configuration implementation of CircleCI. In the beginning, it appeared perplexing, but we eventually understood the purpose of using continuation and path-filtering orbs. In this article, we will share how we utilised the continuation orb to fulfil our requirements with CircleCI.
What were the requirements?
Below were our requirements:
- Weekly trigger
staging-regressionjob onstagingbranch. - Weekly trigger
prod-regressionjob onmasterbranch. - Weekly trigger
staging-regression-other-featuresjob onstagingbranch. - Weekly trigger
prod-regression-other-featuresjob onmasterbranch. - Weekly trigger
sign-up,registration, andsetupjobs onstagingbranch. - As per the need, we should be able to trigger screenshot testing and sanity jobs.
Dynamic Configuration implementation
We created multiple YAML files for our different jobs and workflows. We used the generate_config.js script to choose the workflow file that we wanted to execute. We implemented the below-outlined structure for organising yml files for our different jobs.
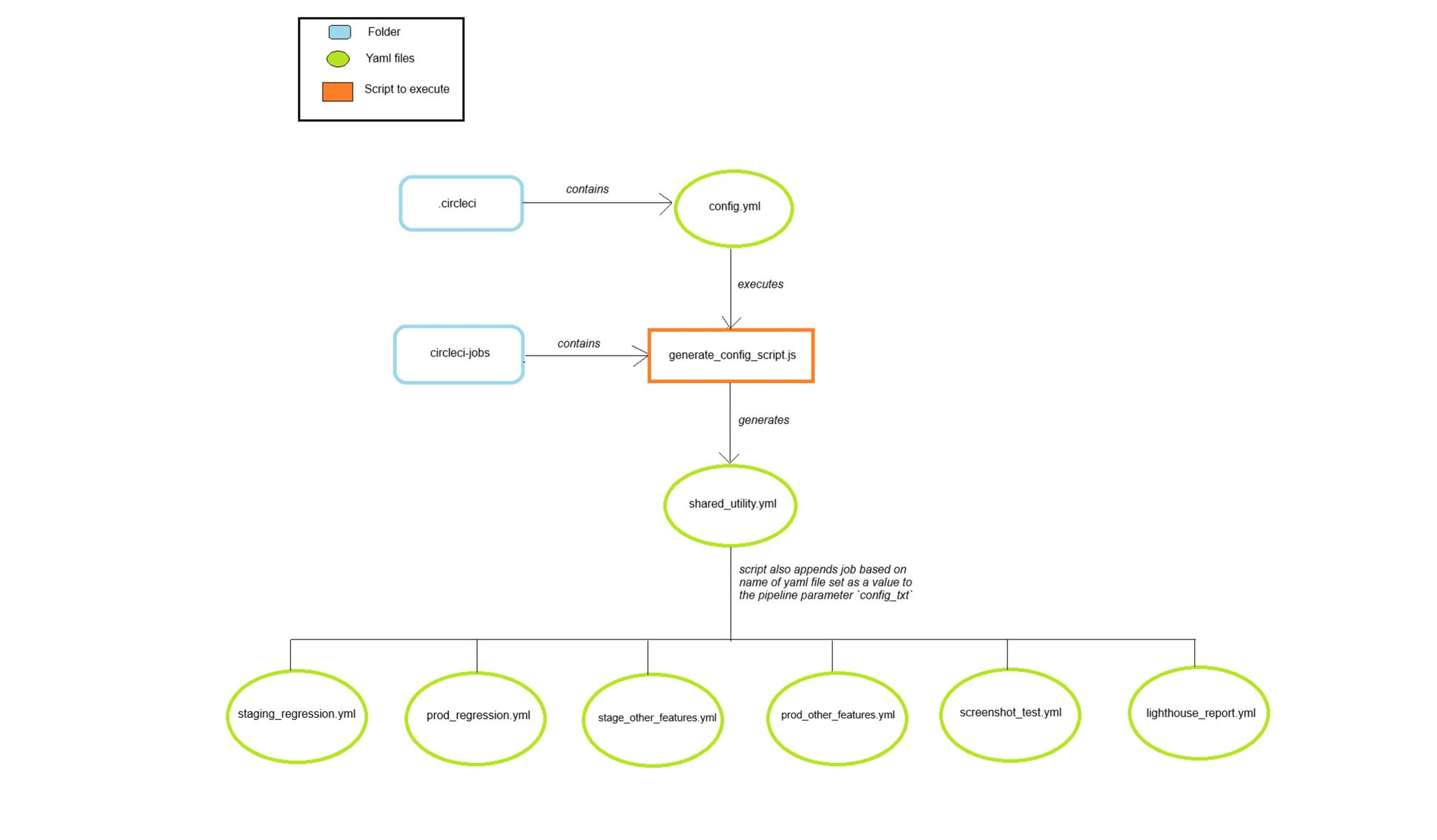
Script to generate a new configuration YAML file based on the parameter
We created a script to generate a new YAML configuration based on the job we want to execute. The new configuration file will be a child configuration file.
/** Below script is implemented in generate_config_script.js file*/
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
function readFile(fileName) {
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, `${fileName}.yml`);
return fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf8');
}
function generateCircleCIConfig() {
const workflow = process.env.CONFIG_TXT;
const workflowConfig = readFile(workflow);
console.log(workflowConfig);
}
generateCircleCIConfig();
The above script is executed from the parent configuration file config.yml present in the .circleci folder.
version: 2.1
setup: true
orbs:
node: circleci/node@5.0.2
continuation: circleci/continuation@0.1.2
parameters:
config_txt:
type: string
default: staging_sanity
jobs:
setup:
docker:
- image: cimg/node:18.16.1-browsers
executor: continuation/default
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Generate config
command: |
node ./circleci-jobs/generate_config_script.js > generated_config.yml
environment:
CONFIG_TXT: << pipeline.parameters.config_txt >>
- continuation/continue:
configuration_path: generated_config.yml
workflows:
setup:
jobs:
- setup
In the above parent config.yml file,
setup: true: This line indicates that the currentconfig.ymlfile is a parent configuration file.- As mentioned in CI Documentation, the
continuationorb is used to execute the child configuration file created based on the output ofgenerate_config_script.js. config_txtis a parameter that is passed togenerate_config_script.js, based on which it creates a child configuration file. The default value isstaging_sanity, so if no explicit parameter value is passed on CircleCI, then it by default triggers thestaging-sanityjob.
Also, make sure to define the parameters declared in the parent config.yml file in the child generated_config.yml file as well. Otherwise, it will throw an error Unexpected argument. The official documentation says Pipeline parameters declared in the setup configuration must also be declared in the continuation configuration. These parameters can be used at continuation time.
In the parent config.yml file, only one workflow can be defined, which is responsible for generating the child configuration file. For our project, we required defining multiple workflows for our jobs, and to achieve the same with dynamic configuration, we used triggers.
Schedule Triggers on CircleCI
-
The next step was to create a scheduled pipeline to periodically trigger a specific job.
-
Pipelines are scheduled to periodically run a specific
jobby adding atriggerfor each of the jobs that need to be executed. -
Triggers are added from the
Triggers Sectionpresent under theProject Settingsoption for theCircleCI Project.
|
- For each of the jobs mentioned above, we created a new
Triggerto periodically run a specific job.
Challenges faced in configuring triggers
We filled out the mandatory information needed to create triggers, but we faced challenges in deciding on the value for the field Repeats Per Hour for the trigger. We were unsure whether this field would trigger the job a certain number of times every hour based on the field's name. We intended our trigger to run just once on the designated day. When we got in touch with CircleCI support, they clarified that the field decides how many times a trigger would be executed in each hour chosen in the Start Time (UTC) selection.
For e.g., if the selected "Start Time (UTC)" is 3:00 (UTC) and 7:00 UTC and "Repeats Per Hour" is set to 2, then the trigger will be executed twice between each selected time, i.e., it will be executed twice between 3:00 (UTC) and 4:00 (UTC) and twice between 7:00 UTC and 8:00 (UTC).
As mentioned in the CI Documentation, setting the start time for a trigger does not guarantee the job will be triggered precisely at the "Start Time" selected. This means that for a trigger, when we select "Start Time" as 6:00 AM UTC and "Repeat Per Hour" as 1, the job will be triggered once between 6:00 AM UTC and 7:00 AM UTC and will not always be triggered exactly at 6:00 AM UTC.
Next, we declared the pipeline parameter named config_txt for our trigger and set its value to the <child_job>.yml file name containing the workflow that we wanted to trigger. For instance, in order to trigger the production regression workflow, we set the config_txt parameter value to prod_regression. Similarly, we created triggers for each workflow that we wanted to execute.
We thought the trigger was scheduled for now. However, the trigger did not execute as scheduled. There was an error block-unregistered-user in our workflow. On investigation, we noticed that for all the triggers, we have "Attribution Actor" set as Scheduled Actor (Scheduling System), which is the default. As mentioned in the article, if the option "Prevent unregistered user spend" is turned ON under the "Usage Control" tab present in the "Plan" section of the project, then the workflow won't be triggered for unregistered users and error block-unregistered-user will be displayed.
This was exactly the case with our project, and to resolve the issue, we selected "Attribution Actor" as one of the users registered in the project. With this, we were able to trigger and execute our workflow successfully.
We have created a demo project circleci-dynamic-configuration-demo that you can clone and explore for better understanding.
References:

